Which choice best describes the polarity of BrF5? This question delves into the fascinating realm of molecular polarity, a fundamental concept in chemistry that governs the behavior and interactions of molecules. As we embark on this exploration, we will uncover the factors influencing the polarity of BrF5, delve into experimental evidence supporting its polarity, and examine the consequences of this polarity on its physical and chemical properties.
The polarity of a molecule arises from the uneven distribution of electrons, creating a separation of positive and negative charges within the molecule. This separation can be attributed to differences in electronegativity, the ability of atoms to attract electrons towards themselves.
In the case of BrF5, the electronegativity of fluorine atoms surpasses that of the bromine atom, resulting in a shift of electron density towards the fluorine atoms.
Define the Concept of Polarity
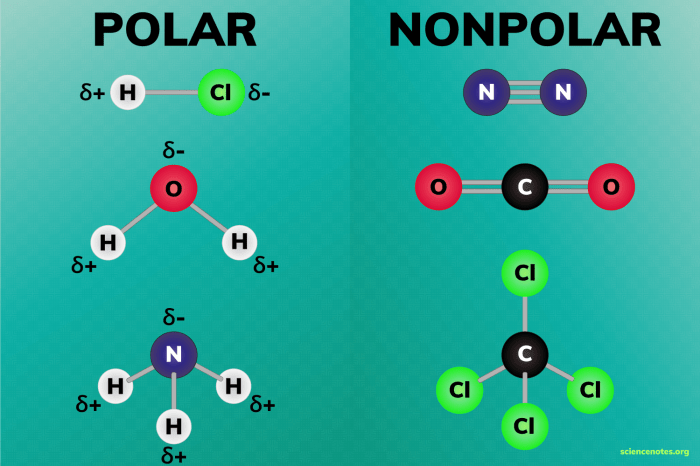
Polarity is a measure of the separation of electric charge within a molecule. A polar molecule has a net positive charge on one end and a net negative charge on the other end. This separation of charge is caused by the electronegativity difference between the atoms in the molecule.
Factors Influencing the Polarity of BrF5
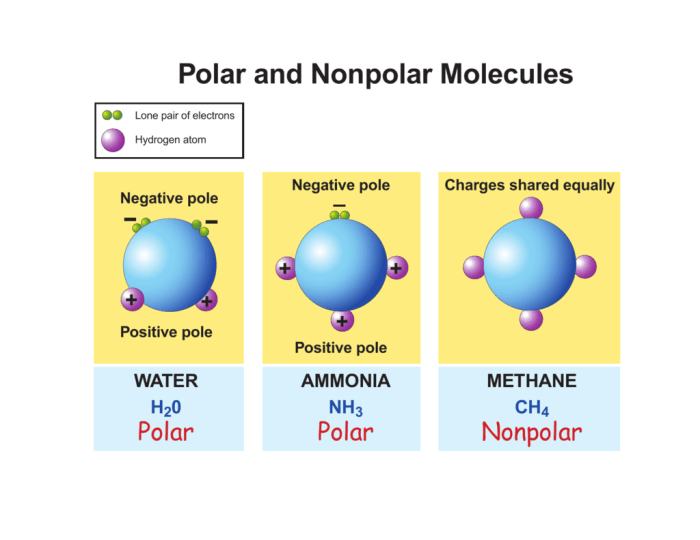
Electronegativity of Bromine and Fluorine Atoms
The electronegativity of an atom is its ability to attract electrons. Bromine is less electronegative than fluorine, so the fluorine atoms in BrF5 will pull the electrons in the bonds towards themselves. This will create a partial negative charge on the fluorine atoms and a partial positive charge on the bromine atom.
Molecular Geometry of BrF5
The molecular geometry of BrF5 is trigonal bipyramidal. This means that the bromine atom is surrounded by five fluorine atoms, with two of the fluorine atoms in the axial positions and three in the equatorial positions. The axial fluorine atoms are more electronegative than the equatorial fluorine atoms, so they will pull the electrons in the bonds towards themselves more strongly.
This will create a greater separation of charge between the axial and equatorial fluorine atoms.
Hybridization of the Bromine Atom
The bromine atom in BrF5 is hybridized sp3d2. This means that the bromine atom has five valence electrons, which are arranged in four sp3 hybrid orbitals and two d orbitals. The sp3 hybrid orbitals are used to form bonds with the five fluorine atoms, while the d orbitals are used to form the axial bonds.
Evidence for the Polarity of BrF5
Dipole Moment Measurements
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of its polarity. The dipole moment of BrF5 is 1.78 D, which indicates that it is a polar molecule.
Reactivity of BrF5 with Polar Solvents
BrF5 is a reactive molecule that can react with polar solvents. This reactivity is due to the polarity of BrF5. The positive end of the BrF5 molecule will be attracted to the negative end of the polar solvent, and the negative end of the BrF5 molecule will be attracted to the positive end of the polar solvent.
Examples of Experimental Data Supporting the Polarity of BrF5
There are a number of experimental data that support the polarity of BrF5. For example, BrF5 has been shown to dissolve in polar solvents, such as water and methanol. BrF5 has also been shown to react with polar molecules, such as ammonia and hydrogen chloride.
Consequences of the Polarity of BrF5: Which Choice Best Describes The Polarity Of Brf5
Role of Polarity in Intermolecular Interactions
The polarity of BrF5 plays a role in its intermolecular interactions. BrF5 will interact with other polar molecules through dipole-dipole interactions. These interactions will be stronger than the van der Waals interactions that occur between nonpolar molecules.
Physical Properties of BrF5, Which choice best describes the polarity of brf5
The polarity of BrF5 affects its physical properties. BrF5 has a higher boiling point and melting point than nonpolar molecules of similar molecular weight. This is because the dipole-dipole interactions between BrF5 molecules are stronger than the van der Waals interactions between nonpolar molecules.
Chemical Reactivity of BrF5
The polarity of BrF5 affects its chemical reactivity. BrF5 is a reactive molecule that can react with a variety of other molecules. The polarity of BrF5 makes it more likely to react with polar molecules than with nonpolar molecules.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of electronegativity in determining molecular polarity?
Electronegativity is a crucial factor in determining molecular polarity. It measures the ability of atoms to attract electrons towards themselves. Differences in electronegativity between atoms within a molecule lead to an uneven distribution of electrons, creating a separation of positive and negative charges, and ultimately resulting in molecular polarity.
How does molecular geometry affect the polarity of a molecule?
Molecular geometry plays a significant role in determining the polarity of a molecule. The arrangement of atoms within a molecule can either amplify or cancel out the individual bond polarities. In the case of BrF5, the T-shaped molecular geometry enhances the polarity of the molecule, as the electronegative fluorine atoms are positioned farther away from the bromine atom, increasing the separation of positive and negative charges.
What experimental techniques can be used to measure the polarity of a molecule?
Various experimental techniques can be employed to measure the polarity of a molecule. One common method is dipole moment measurement. Dipole moment measures the separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule, providing a quantitative assessment of its polarity.
Additionally, spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared and Raman spectroscopy, can provide insights into the polarity of a molecule by analyzing the vibrational and rotational motions of its atoms.