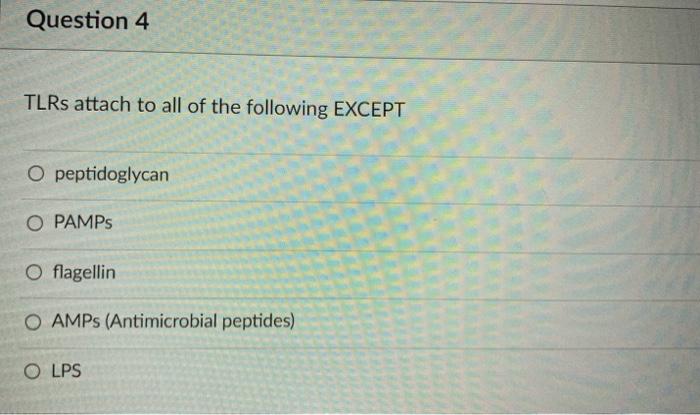
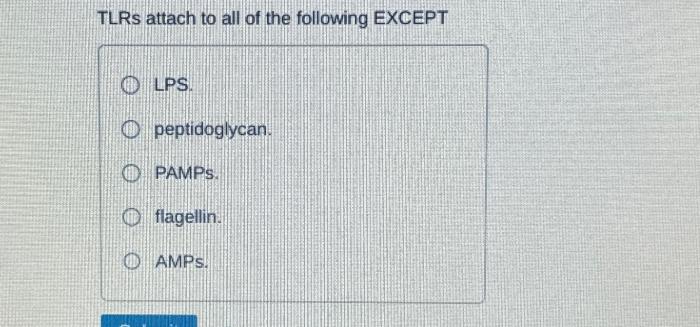
TLRs attach to all of the following except provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of TLRs, their functions, and their role in the immune system. The article also discusses the potential of TLRs as therapeutic targets.
TLRs are a family of proteins that play a critical role in the innate immune system. They are expressed on the surface of immune cells and recognize a wide range of microbial components. When a TLR recognizes its ligand, it triggers a signaling cascade that leads to the activation of immune cells and the production of inflammatory cytokines.
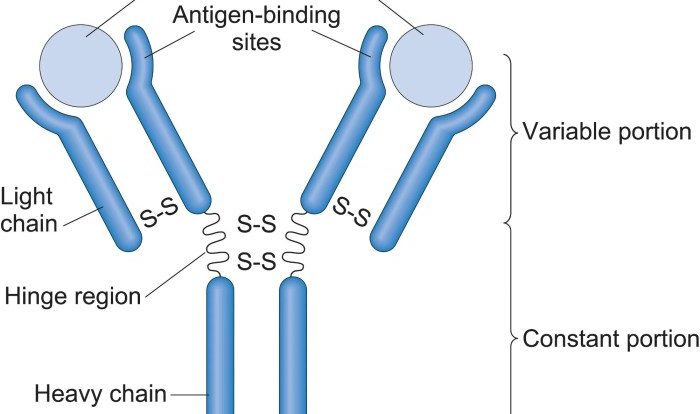
Overview of TLRs
TLRs (Toll-like receptors) are a family of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that play a critical role in the innate immune system. They recognize a wide range of microbial components and danger signals, triggering immune responses to protect the host from infection and tissue damage.
Types of TLRs and their Functions, Tlrs attach to all of the following except
There are 10 known TLRs in humans, each with a specific ligand-binding profile and expression pattern. The following table summarizes the different TLRs, their ligands, and their expression patterns:| TLR | Ligands | Expression ||—|—|—|| TLR1 | Triacyl lipopeptides (TLPs) | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR2 | Lipoproteins, peptidoglycan | Dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils || TLR3 | Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR4 | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) | Macrophages, neutrophils || TLR5 | Flagellin | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR6 | Diacyl lipopeptides (DLPs) | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR7 | Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR8 | Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR9 | Unmethylated CpG DNA | Dendritic cells, macrophages || TLR10 | Unknown | Dendritic cells, macrophages |
TLRs and their Ligands
TLRs recognize their ligands through a variety of mechanisms. Some TLRs, such as TLR4, recognize their ligands directly. Others, such as TLR3, require the assistance of accessory proteins to recognize their ligands.Once a TLR recognizes its ligand, it triggers a signaling cascade that leads to the activation of immune cells.
This signaling cascade can involve the activation of transcription factors, the production of cytokines, and the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection.
TLRs and Immune Responses

TLRs trigger a variety of immune responses, including the production of cytokines, the activation of phagocytes, and the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection.The type of immune response that is triggered by a TLR depends on the specific TLR that is activated.
For example, TLR4 triggers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-12, which promote the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection. TLR3, on the other hand, triggers the production of type I interferons, which inhibit viral replication.
TLRs and Disease

TLRs play a role in the development of a variety of diseases, including sepsis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma.In sepsis, TLRs can trigger the production of excessive amounts of cytokines, which can lead to organ damage and death. In inflammatory bowel disease, TLRs can trigger the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can lead to inflammation and tissue damage.
In asthma, TLRs can trigger the production of type 2 cytokines, which can lead to airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
TLRs and Therapeutics: Tlrs Attach To All Of The Following Except
TLRs are potential therapeutic targets for a variety of diseases. For example, TLR4 inhibitors could be used to treat sepsis, and TLR2 inhibitors could be used to treat inflammatory bowel disease.Several TLR-based therapeutics are currently in development. For example, a TLR4 inhibitor is being developed to treat sepsis, and a TLR2 inhibitor is being developed to treat inflammatory bowel disease.
Detailed FAQs
What are TLRs?
TLRs are a family of proteins that play a critical role in the innate immune system.
What do TLRs do?
TLRs recognize a wide range of microbial components and trigger a signaling cascade that leads to the activation of immune cells and the production of inflammatory cytokines.
What is the role of TLRs in the immune system?
TLRs are essential for the immune system to function properly. They play a role in defending the body against infection, but they can also contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as asthma and arthritis.